Table of contents
Hash Table
What is a Hashtable?
- Hashing is a technique or process of mapping keys/values into the hash table by using a hash function. It is done for faster access to elements. The efficiency of mapping depends on the efficiency of the hash function used.
- Hash tables are a data structure that utilizes key/value pairs. This means every Node or Bucket has both a key and a value.
What is the idea of a Hash table?
- The ability to store key/ value pairs and retrieve the data using the key. This can be done with hash.
- Hash is the ability to encode the key, to reserve a specific location into the data structure, so we can use this hash to retrieve the value directly.
- The hash tables make retrieving data very fast because the time complexity will be O(1).
Hash table terminology:
- Before we start we should learn hash table terminologies:
- Hash: A hash is the result of some algorithm taking an incoming string and converting it into a value that could be used for either security or some other purpose. In the case of a hash table, it is used to determine the index of the array.
- Buckets:A bucket is what is contained in each index of the array of the hash table. Each index is a bucket. An index could potentially contain multiple key/value pairs if a collision occurs.
- Collisions: A collision is what happens when more than one key gets hashed to the same location of the hash table.
Hashing Structure
Hashing
- As we mentioned, the main job of hashing is to turn the key into an integer number, When we do that we should be aware of a couple of things:
- It’s very important that hash codes are deterministic: their output is determined only by their input.
- Hash codes should never have randomness.
- The same key should always produce the same hash code.
- As we mentioned, the main job of hashing is to turn the key into an integer number, When we do that we should be aware of a couple of things:
Creating a Hash
A hashtable traditionally is created from an array. To create a hash table do the following:
- Create an array of size 1024 (the size is important for index placement).
- Do some sort of logic to turn that “key” into a numeric number value. Here is a possible suggestion:
- Add or multiply all the ASCII values together.
- Multiply it by a prime number such as 599.
- Use modulo to get the remainder of the result, when divided by the total size of the array.
- Insert into the array at that index.
For example:
Key = "Cat"
Value = "Josie"
67 + 97 + 116 = 280
280 * 599 = 69648
69648 % 1024 = 16
Key gets placed in an index of 16.
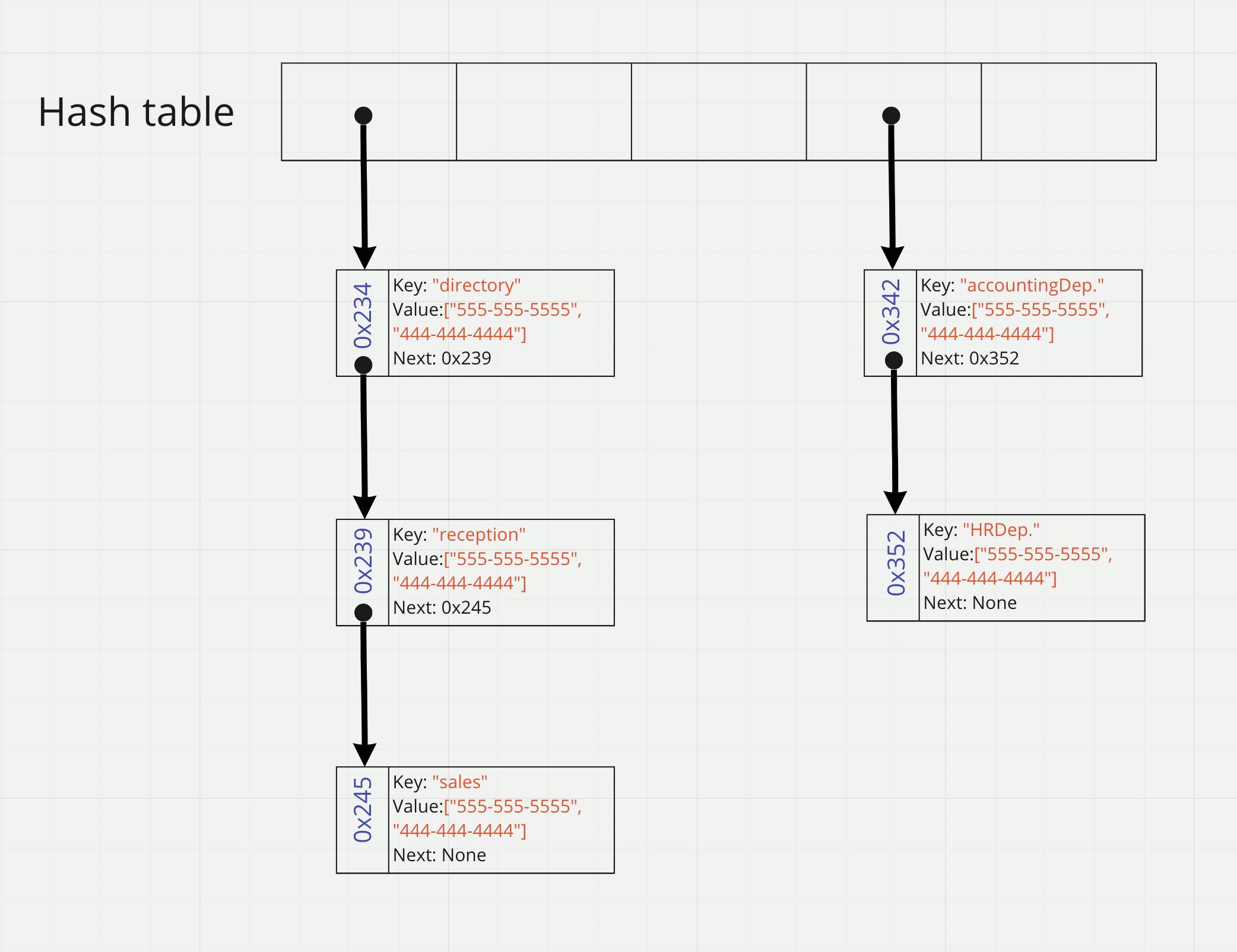
Dive into HOW the key/values are stored in the array.
- As we said above, the bucket refers to the index when we working with hash tables.
- Each bucket holds a key/value pair combination.
- When there is no entry in a specific bucket, the initial value of the bucket will be NULL.
The hash table starts each bucket empty and overwrites its value once a key generates a hashCode that corresponds with an index.
Collisions
- What is Collision?
- Basically, collision refer to the state where we generate two equaled hash.
- What would happen?
- If the collision didn't handle, the last hash will overwrite the bucket.
- How to handle collision
- Collision can be handled by changing the initial state of the buckets.
- So, instead of starting all the buckets as NULL, we can initialize a LinkedList in each one.
- Now, if we generated two equaled hash keys, the key/value pairs can be stored as a node in a linked list.
- So now, the term bucket would be much cleaner.
- Since different keys can lead to the same bucket it’s important to store the entire key/value pair in the bucket, not just the value.
How are hash maps stored and read?
To store hash maps do this:
- Accept a key
- Calculate the hash of the key
- Use modulus to convert the hash into an array index
- Store the key with the value by appending both to the end of a linked list
To read hash map do this:
- Accept a key
- Calculate the hash of the key
- Use modulus to convert the hash into an array index
- Use the array index to access the short LinkedList representing a bucket
- Search through the bucket looking for a node with a key/value pair that matches the key you were given.
Hash table methods
Hash table should have main methods:
- GetHash method
- Add method
- Find method
- Contains method
- Remove method
Code implementation
- Step 1: Create the Node class
class Node: def __init__(self, key, value): self.key = key self.value = value self.next = None - Step 2: Create the HashTable class
- You can change the capacity to satisfies your requirements.
class HashTable: def __init__(self): self.capacity = 70 self.size = 0 self.buckets = [None] * self.capacity
- You can change the capacity to satisfies your requirements.
- Step 3: Create the Hash algorithm.
def get_hash(self, key): hash_sum = 0 # For each character in the key for idx, char in enumerate(key): # Add (index + length of key) ^ (current char code) hash_sum += (idx + len(key)) ** ord(char) # Perform modulus to keep hash_sum in range [0, self.capacity - 1] hash_sum = hash_sum % self.capacity return hash_sum - Step 4: Create the insert method.
def insert(self, key, value): # 1. Increment size self.size += 1 # 2. Compute index of key index = self.get_hash(key) # Go to the node corresponding to the hash node = self.buckets[index] # 3. If bucket is empty: if node is None: # Create node, add it, return self.buckets[index] = Node(key, value) return # 4. Collision! Iterate to the end of the linked list at provided index prev = node while node is not None: prev = node node = node.next # Add a new node at the end of the list with provided key/value prev.next = Node(key, value) - Step 5: Create the find method
def find(self, key):
# 1. Compute hash
index = self.get_hash(key)
# 2. Go to first node in list at bucket
node = self.buckets[index]
# 3. Traverse the linked list at this node
while node is not None and node.key != key:
node = node.next
# 4. Now, node is the requested key/value pair or None
if the node is None:
# Not found
return None
else:
# Found - return the data value
return node.value
- Step 6: Create remove method.
def remove(self, key): # 1. Compute hash index = self.get_hash(key) node = self.buckets[index] prev = None # 2. Iterate to the requested node while node is not None and node.key != key: prev = node node = node.next # Now, node is either the requested node or none if node is None: # 3. Key not found return None else: # 4. The key was found. self.size -= 1 result = node.value # Delete this element in linked list if prev is None: node = None else: prev.next = prev.next.next # Return the deleted language return result
Representation of the hash table